Shoulder dislocation


Mitsutoshi Hayashi
Mitsutoshi Hayashi
Doctor of Medicine, specialist in the Japanese Society of Rehabilitation Medicine, specialist in the Japanese Society of Orthopaedic Surgery, specialist in the Japanese Society of Rheumatology, staff to strengthen JOC, and sports physician certified by the Japan Sports Association
肩關節脫位
关节稳定性较低的肩关节,如果受到后方强有力的外力作用就会发生肩关节脱位,多见于橄榄球、美式橄榄球、柔道等接触型运动。
疾病概述
疾病的概念
肩關節一般是指位於肱骨近端部分(靠近面部)的肱骨頭和作為接收盤的肩胛骨關節盂組成的盂肱關節。它是人體中關節活動範圍最廣的結構,而肩關節的骨頭結構又比較淺,所以需要通過關節韌帶、肌肉(腱板)來加固關節周圍。當通過運動等施加強大的外力時,就很容易引起破裂、脫位。
病因和發病機制
受傷原因
受傷多發於橄欖球、美式橄欖球、柔道、手球等接觸型運動,也會因為滑冰、單板滑雪的跌倒而引發。
在肩關節上舉狀態(雙手舉起的狀態)下從後方施加外力、從後方拽手、摔倒時手撐在後方等情況下,處於不穩定狀態的肱骨頭從關節面滑脫導致脫位。脫位的類型多為肱骨頭移動到身體前面的前方脫位型(照片1)。
首次受傷是因為後方強外力的施加而導致的,但是第二次以後的受傷卻會因為關節制動結構(骨、韌帶、關節囊)的磨損,即使比首次弱的外力,也會引起脫位。每次反复時這種趨勢變得更加明顯,即使是比較輕微的外力也容易導致再次脫位(反复性脫位)。
症狀
急劇的疼痛、腫脹、畸形、運動受限(彈簧樣固定)、作為並發損傷也可見血液循環障礙、神經麻痺(肩、手指麻木)。
診斷
通過X射線、應力拍片檢查關節面的適宜性。最近通過CT、MRI檢查(照片2),可以很容易掌握軟骨組織的損傷程度。
另外,確認對關節穩定性很重要的肩胛骨關節盂下緣前方(Bankart照片4)和肱骨頭後外側(Hill-Sachs)的損傷也是有必要的。
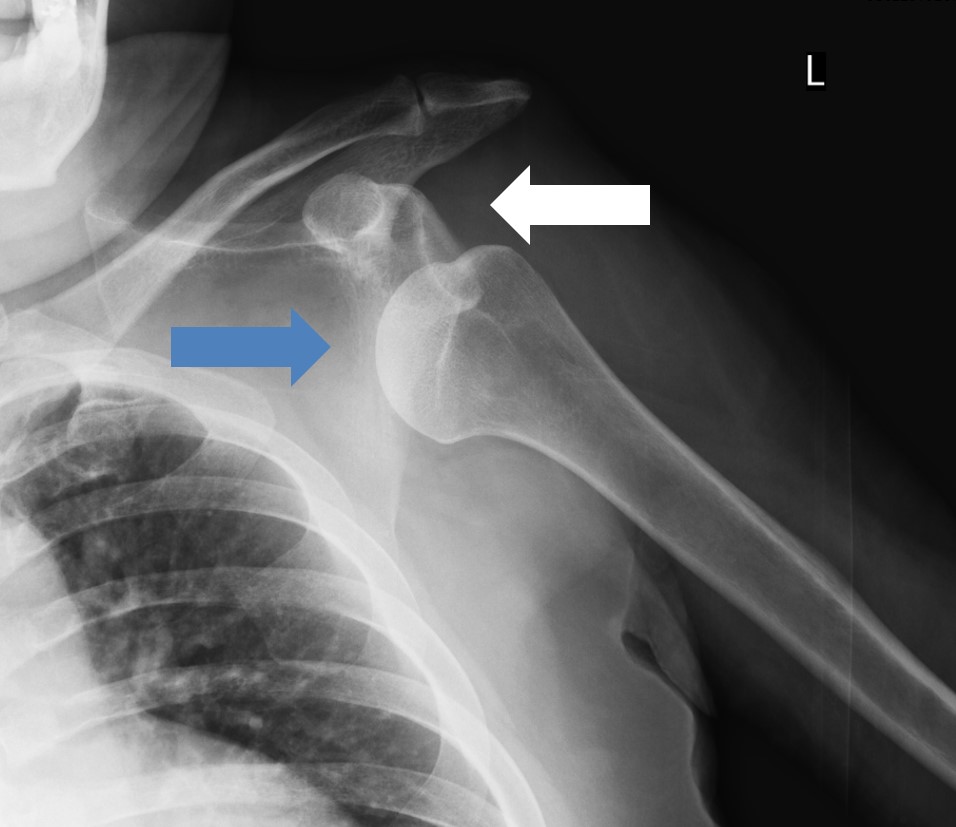
照片1 左肩關節脫位(白色箭頭是骨頭本來的位置)
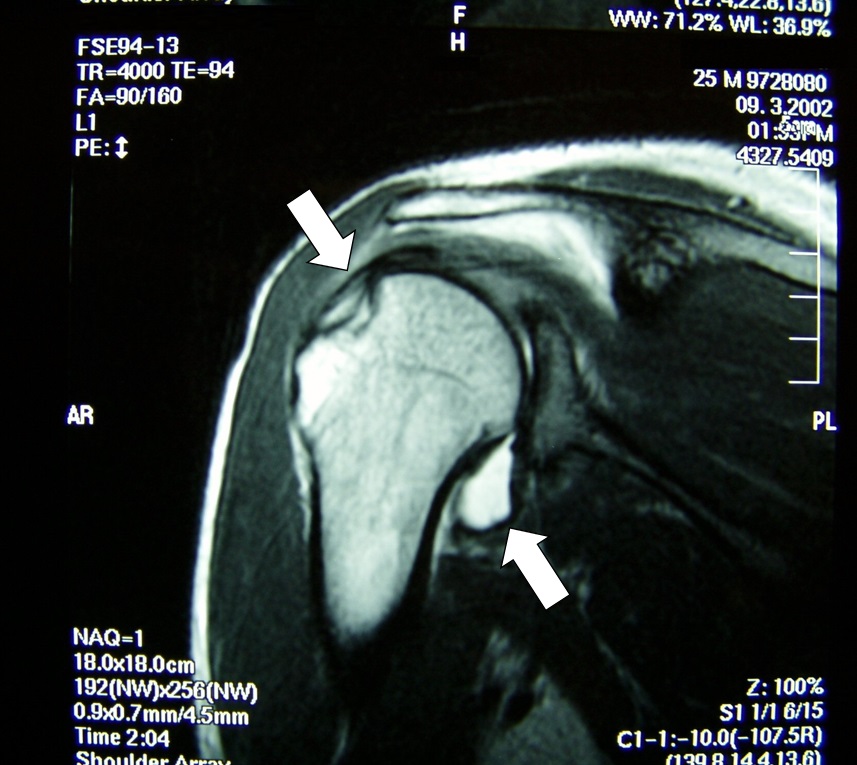
照片2 整復後的MRI圖像。肱骨周圍由於出血顯示為高信號(白色)
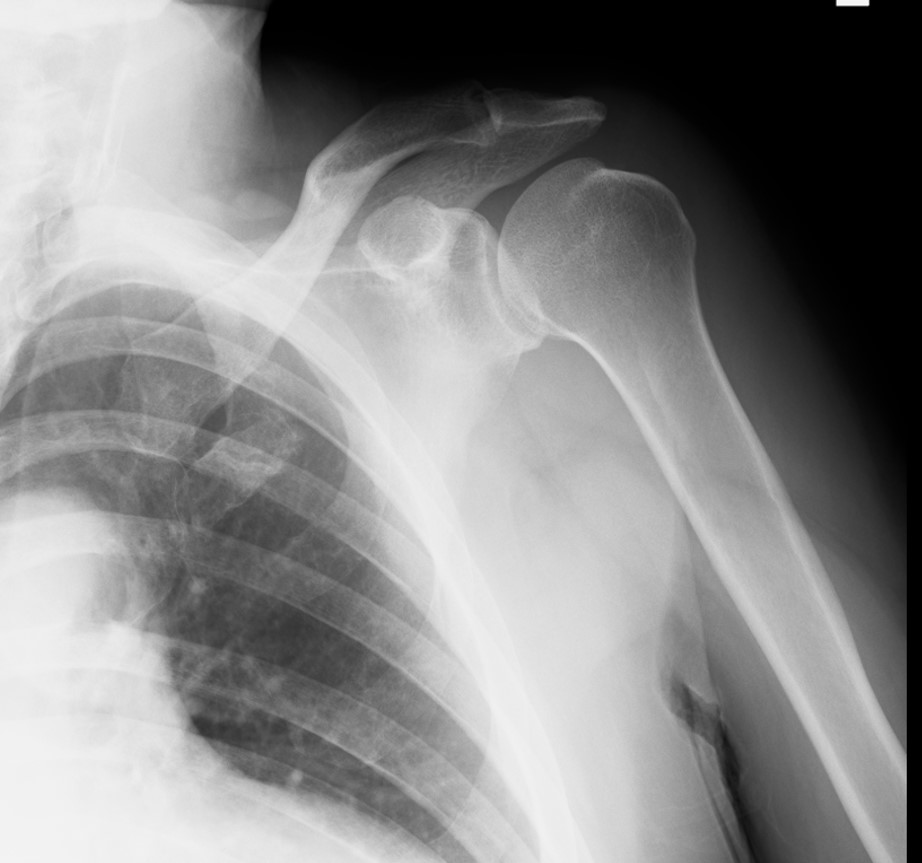
照片3 左肩關節脫位整復後的X光照片
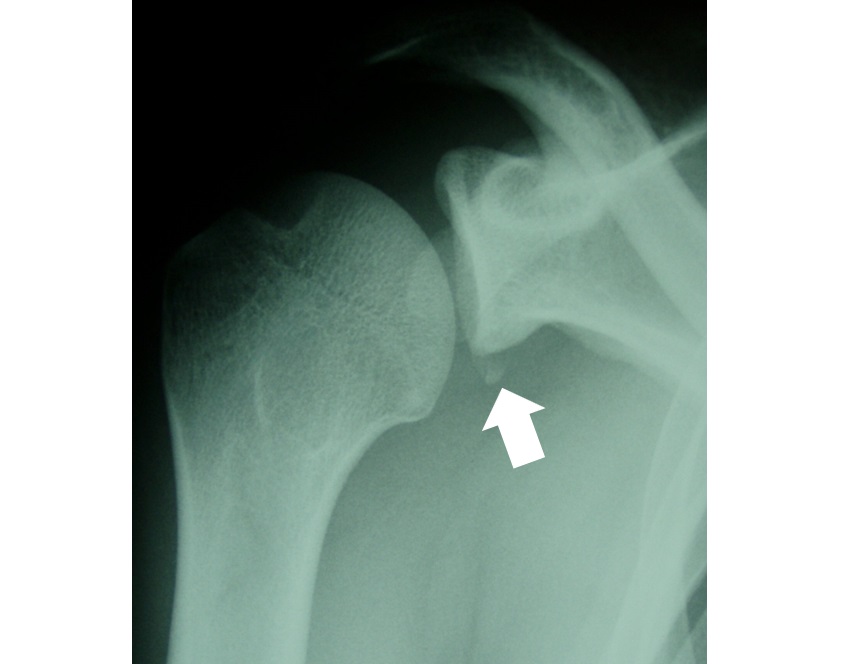
照片4 關節邊緣的撕脫骨折。或者說是肩胛骨關節盂下緣前方骨折
治療和康復
治療
治療大致可分為保守治療和手術治療。首次受傷時,採用保守的徒手整復後,上臂下垂,保持肩關節內旋姿勢,使用三角巾等進行3-4週的Desault固定(Desault:照片5),實施局部修復、謀求穩定的保守療法。再次脫位時也要進行約3週左右的固定。如果第一次的固定時間不充分、康復訓練不適當,容易引起再次脫位甚至反复脫位,要引起注意。手術治療通常是在反复脫位的情況下實施。術後需要6個月才能恢復接觸型競技。
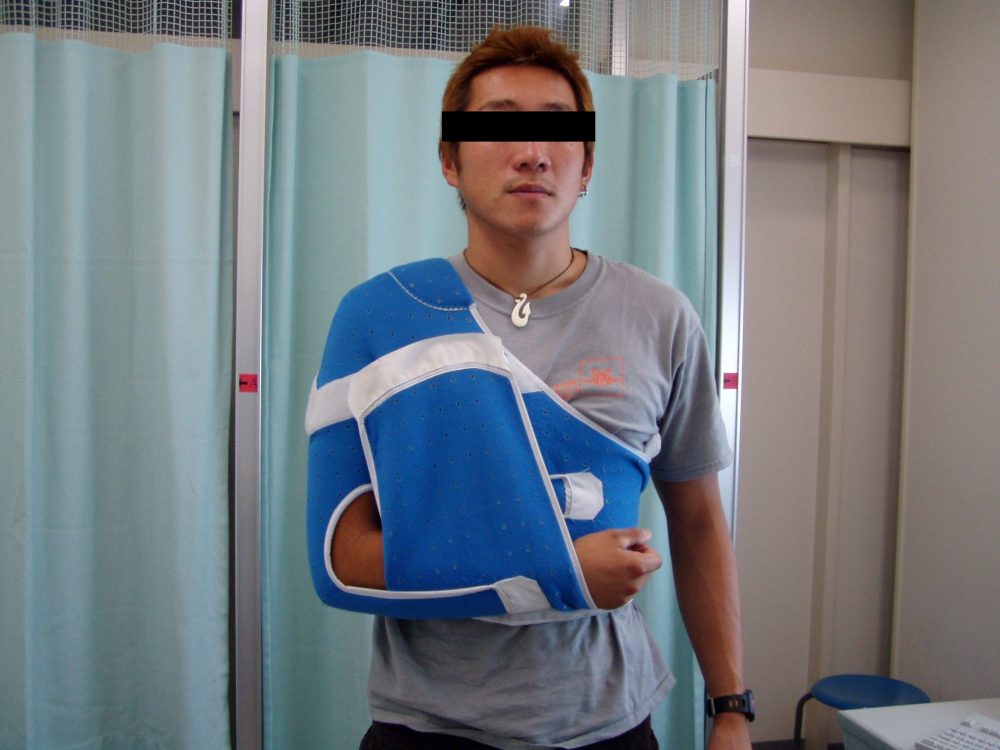
照片5 使用吊帶進行Desault固定
預後
反复脫位從首次開始2年內復發率很高,有6成患者自述是因為關節不穩定。
(摘自2014年美國骨科協會)。
康復訓練
受傷後在不影響損傷部位的範圍內,從手指運動開始。受傷1週後,開始肩關節內轉、內旋姿勢的等軸訓練,3週後,進行肩關節上舉90度範圍內的輕微運動。脫位後康復訓練的要點是背靠牆壁或地板,手在身體前方區域內的上肢訓練。成為受傷動作的肩關節前方上舉外轉、外旋的動作,直到康復訓練的最終階段(約6週)是被禁止的。

Hitoshi Takahashi
Hitoshi Takahashi
Associate Professor, the Department of Regional Medicine, Teikyo Heisei University
A certified athletic trainer from the Japan Sport Association, a practitioner of acupuncture and a massage practitioner
Dislocation of shoulder joint (trainer stitch)
On-site evaluation and first aid
Shoulder dislocations occur when the shoulder joint is excessively abducted and externally rotated due to tackles or falls. Patients are unable to actively rotate it in the outward direction. Making assessment of the injury is easier because a part of the shoulder appears depressed between the acromion and upper arm. Even if reduction is possible at the sports site, it is always necessary to check for complications and seek medical attention. It is important to note that, after a first dislocation, inadequate treatment and rehabilitation often lead to recurrent dislocations of the shoulder.
Reconditioning
Athletic rehabilitation
The purpose of athletic rehabilitation of shoulder dislocations (shoulder instability) is to acquire joint stability after gaining range of motion and strength. The joints may be stabilized by ligaments, which are responsible for static stability, and by muscles, which are responsible for dynamic stability. In athletic rehabilitation, it is important to increase dynamic stability, to obtain not only improvement in muscle strength, but also improvement in neuromuscular coordination through training of proprioceptors.
This section presents basic programs to improve neuromuscular coordination and stabilize the shoulder joint. It is important to gradually apply stress depending on the condition of the affected area and the presence or absence of anxiety in the athlete.
Training of proprioceptors
Proprioceptors are found in the joint capsule, ligaments, muscles, tendons, and skin and serve as sensors for external stimuli (e.g., tactile pressure, pain, and temperature sensation) and internal body conditions (e.g., muscle tendon length, joint position). Proprioceptors transmit such information to the center (brain), where the center directs the information to the muscles, and the muscles move reflexively.
The function of these proprioceptors → central nervous → muscular reflex mechanisms (neuromuscular coordination) is closely related to postural control, body protection (avoidance of injury), and joint stability. Consequently, damaging ligaments and joint capsule and impairing proprioceptors can reduce neuromuscular coordination and prevent the body from responding instantaneously to the unexpected external forces produced by sporting activities.
Thus, proper receptor training is effective not only for athletic rehabilitation, but also for preventing injuries and disabilities from occurring on a daily basis.
Stabilization training
Perform 3 to 5 sets of each exercise for 3 minutes.
Supine position
Put your arm in a supine position. The trainer holds the wrist and applies external force in various directions. The trainer should not apply sudden, because large forces or instantaneous twisting movements. The appropriate force, which the patient can maintain the position is applied by the trainer.
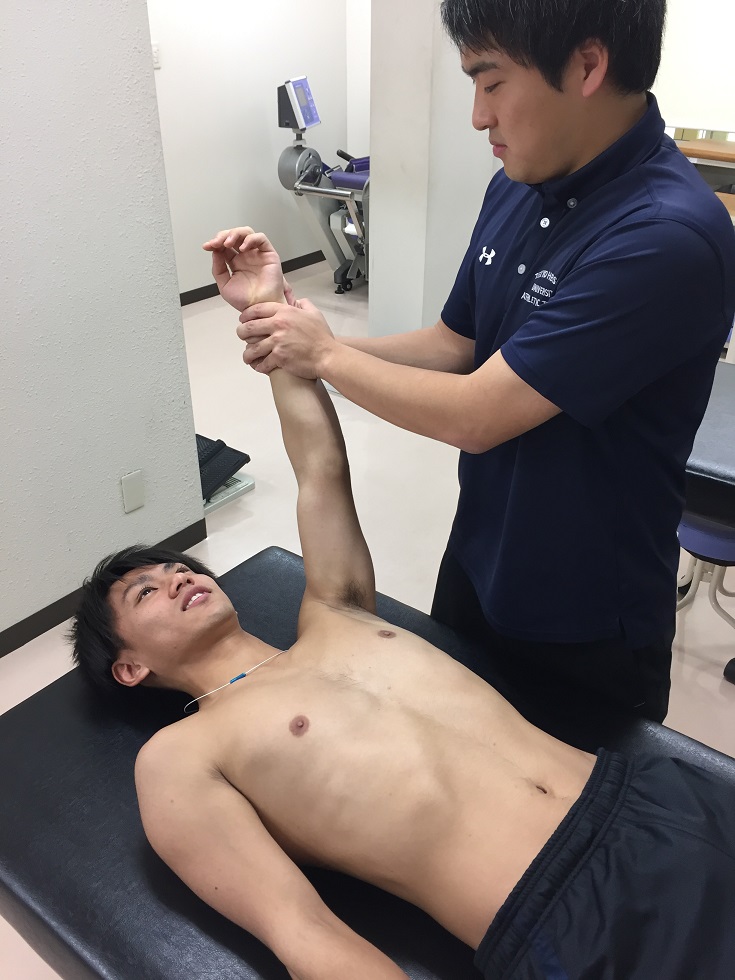
Hold the wrist and provide external force in various directions.
〇 Crawling for all fours
Next, crawling for all fours is done with fixing the scapula by putting the force around the scapula in order to prevent it from floating of the scapula.
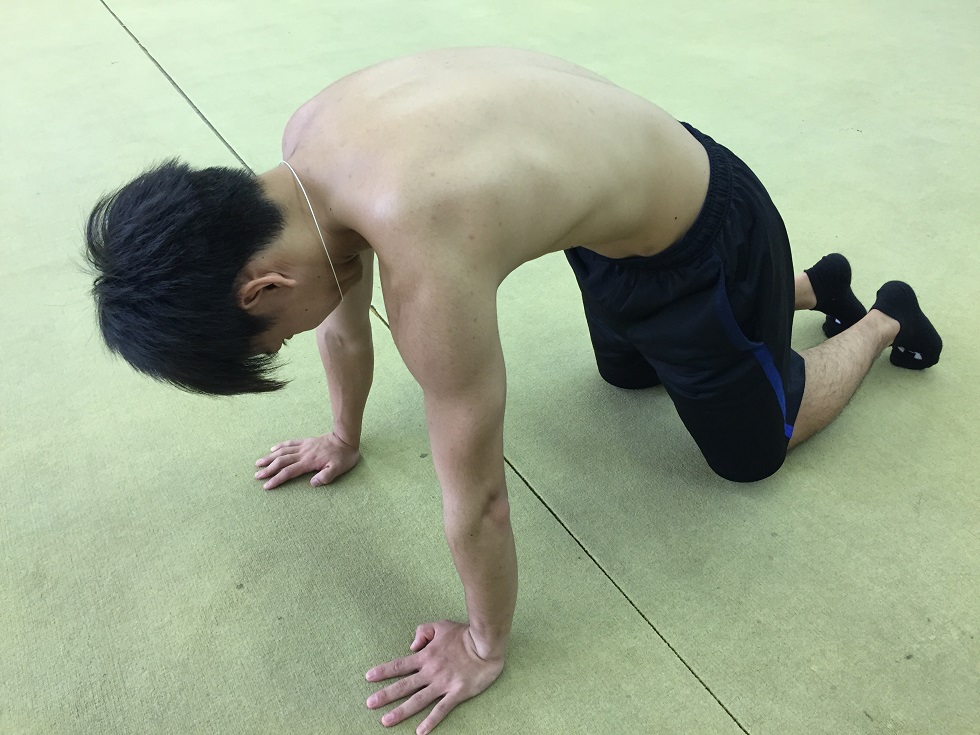

Correct posture
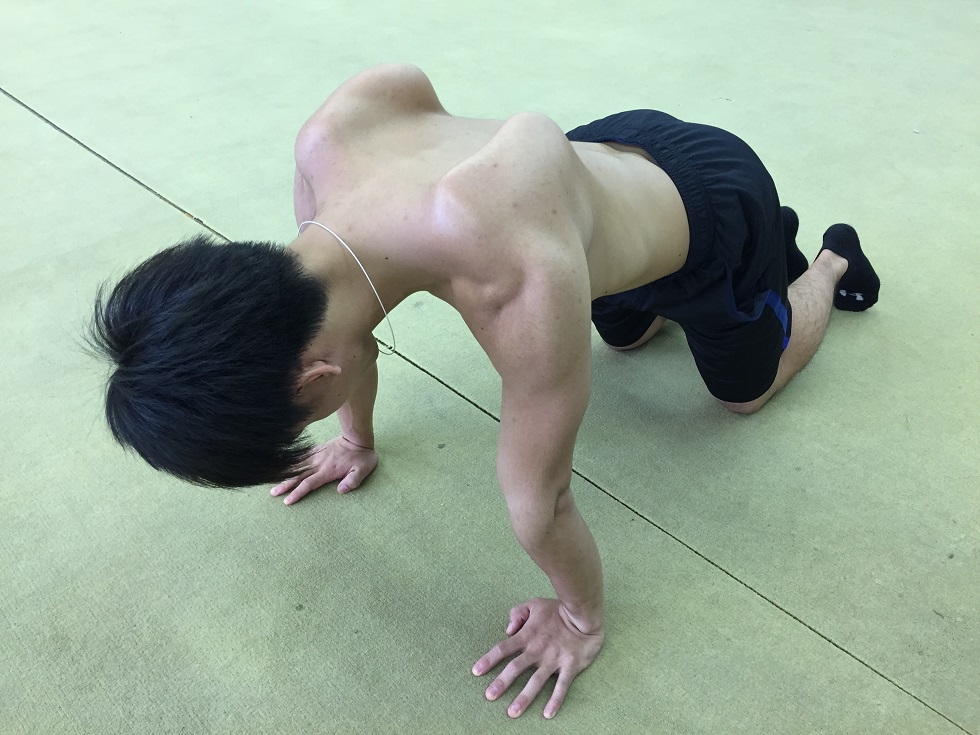

Incorrect position with the scapula floating up
The trainer holds the shoulder joint and provides external force. Also, the holding prevents falls due to lack of balance. If the patient gets used, the levels of exercise raises step by step by using balancing disks to add unstable elements to the step-by-step process.
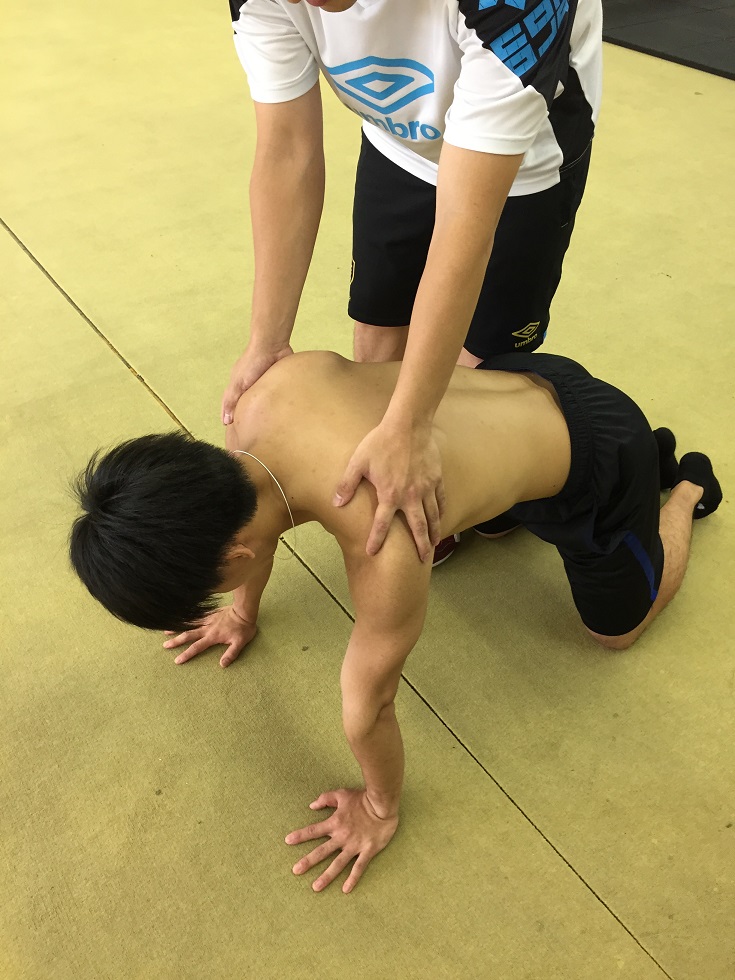
Hold the shoulder joint and apply external force.
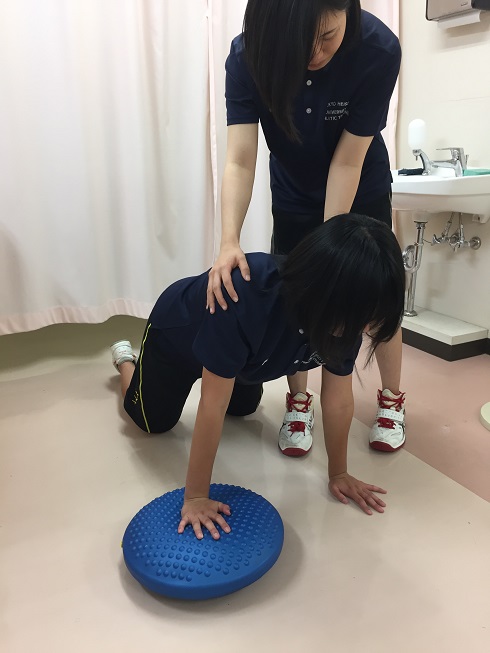

Balancing disks are used in the following order: healthy side - affected side - both sides
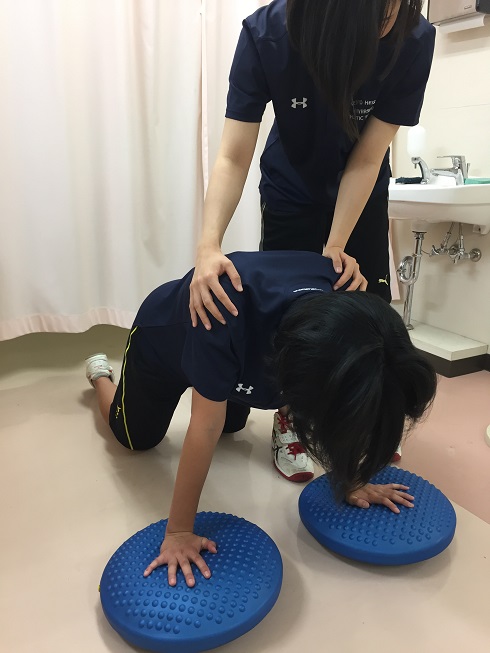
Pattern on both sides

